|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|






Organ Systems and Organs

Before one can understand how xenobiotics affect these different body components, knowledge of normal body components and how they function is necessary. For this reason, this section provides a basic overview of
anatomy and physiology as it relates to toxicity mechanisms. The basic structure and functional organization of the human body can be thought of as a pyramid or hierarchical arrangement in which the lowest level of organization (the foundation) consists of cells and chemicals. Organs and organ systems represent the highest levels of organization. This is illustrated below.
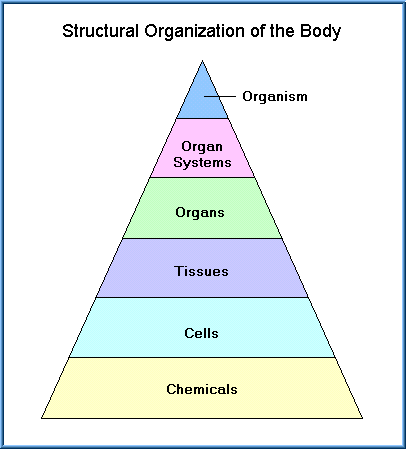
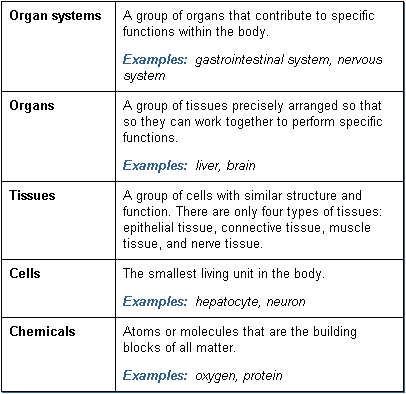
Simplified definitions of the various levels of organization within the body are:
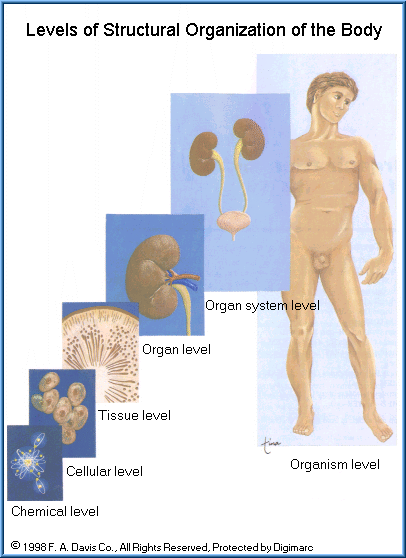
The following figure illustrates the hierarchical organization of these body components.
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |

V. C. Scanlon and T. Sanders, Essentials of
Anatomy and Physiology, 2nd edition. F. A. Davis, 1995. |
|
The human body consists of eleven organ systems, each which contains several specific organs. An organ is a unique anatomic structure consisting of groups of tissues that work in concert to perform specific functions. Listed below are the eleven organ systems and their specific organs.
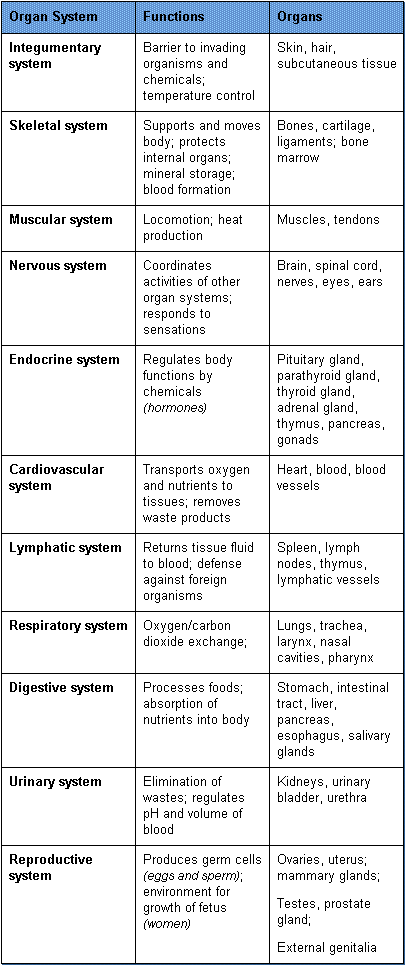

|
|
|
|